
Description:
Comparison operators are used in conditions
that compare one expression to another value or expression. They are used in
the WHERE clause.
Syntax:
... WHERE expr operator value
Examples:
SELECT last_name, salary
FROM employees
WHERE salary <= 3000;
The SELECT
statement retrieves the last name and salary from the EMPLOYEES table for any
employee whose salary is less than or equal to $3,000. Note that there is an
explicit value supplied to the WHERE clause. The explicit value of 3000 is
compared to the salary value in the SALARY column of the EMPLOYEES table.
SELECT last_name, salary
FROM employees
WHERE salary BETWEEN 2500 AND 3500 ;
The SELECT
statement returns rows from the EMPLOYEES table for any employee whose salary
is between $2,500 and $3,500.
Values that
are specified with the BETWEEN operator are inclusive. However, you must
specify the lower limit first.
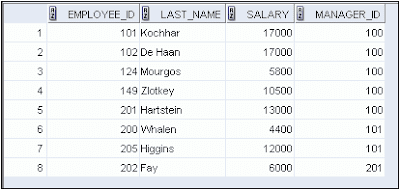
SELECT employee_id,last_name, salary,
manager_id
FROM employees
WHERE manager_id IN (100, 101, 201) ;
The SELECT
statement displays last names, salaries, and managers’ employee numbers for all
the employees whose manager’s employee number is 100, 101, or 201.
The IN operator is internally
evaluated by the Oracle server as a set of OR conditions, such as a=value1 or
a=value2 or a=value3.
SELECT last_name
FROM employees
WHERE last_name LIKE '_o%' ;
% denotes zero or many characters.
_ denotes one character.
The SELECT
statement displays the
names of all employees whose last names have the letter "o" as the second
character.
SELECT last_name,
manager_id
FROM employees
WHERE manager_id IS NULL ;
A null value means that the value is unavailable, unassigned,
unknown, or inapplicable. Therefore, you cannot test with =,
because a null cannot be equal or unequal to any value.
The SELECT
statement displays the last names and managers of all employees who do not have
a manager.











No comments :
Post a Comment